SAP XI provides different ways for SAP systems to communicate via SAP XI. You have three options namely IDoc Adapters, RFC Adapters and Proxies. In one of the earlier posts that spoke about your first XI scenario, we learned configuring the IDoc receiver adapter. And in the coming articles, I shall throw light on different adapters. This article specifically deals with understanding basics of RFC adapter on sender and the receiver side.
 RFC Adapter converts the incoming RFC calls to XML and XML messages to outgoing RFC calls. We can have both synchronous (sRFC) and asynchronous (tRFC) communication with SAP systems. The former works with Best Effort QoS (Quality of Service) while the later by Exactly Once (EO).
RFC Adapter converts the incoming RFC calls to XML and XML messages to outgoing RFC calls. We can have both synchronous (sRFC) and asynchronous (tRFC) communication with SAP systems. The former works with Best Effort QoS (Quality of Service) while the later by Exactly Once (EO).
Unlike IDoc adapter, RFC Adapter is installed on the J2EE Adapter Engine and can be monitored via Adapter Monitoring and Communication Channel Monitoring in the Runtime Workbench.
Now let us understand the configuration needed to set up RFC communication.
RFC Sender Adapter
In this case, Sender SAP system requests XI Integration Engine to process RFC calls. This could either be synchronous or asynchronous.
On the source SAP system, go to transaction SM59 and create a new RFC connection of type ‘T’ (TCP/IP Connection). On the Technical Settings tab, select “Registered Server Program” radio button and specify an arbitrary Program ID. Note that the same program ID must be specified in the configuration of the sender adapter communication channel. Also note that this program ID is case-sensitive.
When using the RFC call in your ABAP program you should specify the RFC destination created above. For example,
CALL FUNCTION ‘<NAME_OF_THE_RFC_FUNCTION_MODULE>’
DESTINATION ‘<RFC_DESTINATION_NAME>’.
Also, in case you are setting up asynchronous interface, the RFC should be called in the background. For example,
CALL FUNCTION ‘<NAME_OF_THE_RFC_FUNCTION_MODULE>’
IN BACKGROUND TASK
DESTINATION ‘<RFC_DESTINATION_NAME>’.
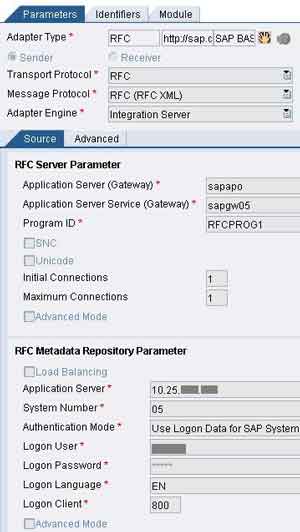
 Now, create the relevant communication channel in the XI Integration Directory. Select the Adapter Type as RFC Sender (Please see the figure above). Specify the Application server and Gateway service of the sender SAP system. Specify the program ID. Specify exactly the same program ID that you provided while creating the RFC destination in SAP system. Note that this program ID is case-sensitive. Provide Application server details and logon credentials in the RFC metadata repository parameter. Save and activate the channel. Note that the RFC definition that you import in the Integration Repository is used only at design time. At runtime, XI loads the metadata from the sender SAP system by using the credentials provided here.
Now, create the relevant communication channel in the XI Integration Directory. Select the Adapter Type as RFC Sender (Please see the figure above). Specify the Application server and Gateway service of the sender SAP system. Specify the program ID. Specify exactly the same program ID that you provided while creating the RFC destination in SAP system. Note that this program ID is case-sensitive. Provide Application server details and logon credentials in the RFC metadata repository parameter. Save and activate the channel. Note that the RFC definition that you import in the Integration Repository is used only at design time. At runtime, XI loads the metadata from the sender SAP system by using the credentials provided here.
RFC Receiver Adapter
In this case, XI sends the data in the RFC format (after conversion from XML format by the receiver adapter) to the target system where the RFC is executed.
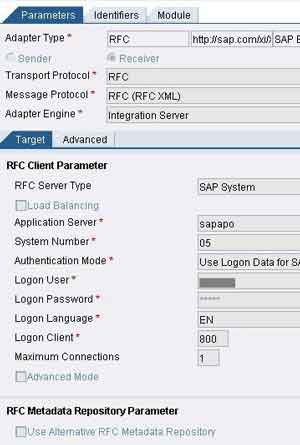
Configuring the receiver adapter is even simpler. Create a communication channel in ID of type RFC Receiver (Please see the figure above on the left). Specify the RFC Client parameters like the Application server details, logon credentials etc and activate the channel.
Testing the Connectivity
Sometimes, especially when new SAP environments are setup, you may want to test their RFC connectivity to SAP XI before you create your actual RFC based interfaces/scenarios. There is a quick and easy way to accomplish this.
 Create a RFC destination of type ‘T’ in the SAP system as described previously. Then, go to XI Integration Repository and import the RFC Function Module STFC_CONNECTION from the SAP system. Activate your change list.
Create a RFC destination of type ‘T’ in the SAP system as described previously. Then, go to XI Integration Repository and import the RFC Function Module STFC_CONNECTION from the SAP system. Activate your change list.
Configure sender and receiver communication channels in ID by specifying the relevant parameters of the SAP system as discussed previously. Remember that the Program ID in sender communication channel and RFC destination in SAP system must match (case-sensitive).
 Accordingly, complete the remaining ID configuration objects like Sender Agreement, Receiver Determination, Interface Determination and Receiver Agreement. No Interface mapping is necessary. Activate your change list.
Accordingly, complete the remaining ID configuration objects like Sender Agreement, Receiver Determination, Interface Determination and Receiver Agreement. No Interface mapping is necessary. Activate your change list.
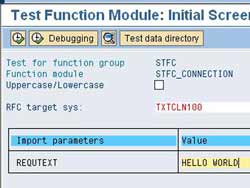
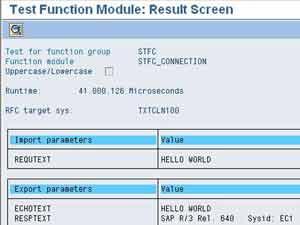
Now, go back to the SAP system and execute the function module STFC_CONNECTION using transaction SE37. Specify the above RFC destination in ‘RFC target sys’ input box. You can specify any arbitrary input as REQUTEXT. If everything works fine, you should receive the same text as a response. You can also see two corresponding messages in SXMB_MONI transaction in SAP XI. This verifies the connection between SAP system and SAP XI.